Magnesium: What It Is, Benefits, and How to Incorporate It Into Your Life
Magnesium is one of the most vital minerals for maintaining a healthy body and mind. Often referred to as the “miracle mineral,” magnesium is involved in over 300 enzymatic processes in the body. Despite its importance, magnesium deficiency is widespread, impacting energy levels, mental health, and physical well-being. This comprehensive guide will explore what magnesium is, its types and uses, the symptoms of magnesium deficiency, and the 27 incredible benefits it offers.
This post contains affiliate links. I may earn a small commission, at no extra cost to you.


What Is Magnesium?
Magnesium is an essential mineral found in the earth, sea, plants, animals, and humans. It plays a critical role in various bodily functions, including energy production, muscle contraction, nerve function, and bone development. Magnesium is primarily stored in bones (about 60%) and soft tissues, with only 1% circulating in the bloodstream.
Why Is Magnesium Important?
Magnesium is crucial for maintaining optimal health because it:
- Helps convert food into energy.
- Supports DNA and protein synthesis.
- Maintains healthy muscles and nerves.
- Regulates blood sugar and blood pressure levels.
- Plays a role in mood regulation and brain function.
Despite its importance, many people fail to meet their daily magnesium needs, leading to magnesium deficiency.
Magnesium Deficiency and Its Symptoms
Magnesium deficiency occurs when your body doesn’t get enough magnesium through diet or supplements. It can develop over time due to poor diet, stress, or certain health conditions.
Common Symptoms of Magnesium Deficiency:
- Muscle cramps and spasms.
- Fatigue or low energy.
- Weakness.
- Irregular heartbeat.
- Anxiety or depression.
- Insomnia or poor sleep quality.
- Migraines or headaches.
- Numbness or tingling.
- High blood pressure.
- Poor digestion or constipation.
If you recognize these magnesium deficiency symptoms, it’s time to evaluate your magnesium intake and consider incorporating more magnesium-rich foods or supplements into your routine.

Magnesium-Rich Foods
One of the easiest ways to boost your magnesium levels is through diet. Foods naturally rich in magnesium include:
- Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, pumpkin seeds, and cashews.
- Legumes: Lentils, chickpeas, and black beans.
- Whole Grains: Brown rice, quinoa, and oats.
- Fruits: Bananas, avocados, and figs.
- Seafood: Salmon, mackerel, and halibut.
- Dark Chocolate: Rich in magnesium and antioxidants.
- Tofu: A plant-based protein source high in magnesium.

Including these magnesium-rich foods in your daily meals can help ensure you meet your recommended magnesium intake.
Types of Magnesium and Their Uses
Magnesium comes in several forms, each suited to specific needs. Understanding the different types can help you choose the best one for your goals:
- Magnesium Glycinate: Known for its calming effects, it’s ideal for improving sleep, reducing anxiety, and promoting relaxation.
- Magnesium Citrate: Often used as a natural laxative to relieve constipation.
- Magnesium Malate: Helps with energy production and muscle function, making it great for athletes.
- Magnesium Threonate: Known for its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier, it supports cognitive function and memory.
- Magnesium Chloride: Found in magnesium oil and sprays, it’s great for topical application.
- Magnesium Oxide: Used to relieve heartburn and indigestion.
- Magnesium Sulfate: Commonly known as Epsom salt, it’s used for muscle relaxation in baths.


27 Incredible Benefits of Magnesium
1. Boosts Energy Production
Magnesium is essential for converting food into energy, making it a critical nutrient for staying active and alert.
2. Improves Sleep Quality
Magnesium glycinate benefits include promoting relaxation and improving sleep by calming the nervous system.



3. Reduces Stress and Anxiety
Magnesium plays a role in regulating neurotransmitters, which helps reduce stress and anxiety levels.
4. Supports Bone Health
Magnesium works alongside calcium and vitamin D to strengthen bones and prevent osteoporosis.
5. Relieves Muscle Cramps
Magnesium helps relax muscles, making it an effective remedy for cramps and spasms.


6. Regulates Blood Pressure
Adequate magnesium levels can lower high blood pressure and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
7. Enhances Brain Function
Magnesium threonate improves cognitive abilities, memory, and focus by supporting brain cell health.
8. Prevents Migraines
Magnesium can reduce the frequency and severity of migraines by relaxing blood vessels.
9. Aids Digestion
Magnesium citrate is commonly used to relieve constipation and promote regular bowel movements.
10. Alleviates PMS Symptoms
Magnesium reduces bloating, mood swings, and other symptoms of premenstrual syndrome (PMS).
11. Supports Heart Health
Magnesium regulates heart rhythm and prevents arrhythmias.
12. Improves Insulin Sensitivity
Magnesium helps regulate blood sugar levels and supports insulin sensitivity, making it beneficial for people with diabetes.
13. Reduces Inflammation
Magnesium’s anti-inflammatory properties help reduce chronic inflammation, which is linked to various diseases.
14. Promotes Healthy Skin
Using magnesium lotion or oil can hydrate the skin, reduce acne, and promote a healthy complexion.
15. Relaxes Muscles
Epsom salt baths or magnesium sprays can soothe sore muscles after exercise.
16. Enhances Exercise Performance
Magnesium improves oxygen uptake and energy production, boosting endurance and performance.
17. Strengthens Immune Function
Magnesium supports immune cell activity, helping the body fight infections and illnesses.
18. Prevents Kidney Stones
Magnesium inhibits the formation of kidney stones by balancing calcium levels.
19. Improves Mood
Magnesium deficiency is linked to depression. Supplementing with magnesium can improve mood and mental well-being.
20. Supports Healthy Pregnancy
Magnesium aids fetal development and reduces the risk of complications like preeclampsia.
21. Eases Arthritis Symptoms
Magnesium reduces joint inflammation and pain associated with arthritis.
22. Protects Against Asthma
Magnesium relaxes the airways, reducing asthma symptoms and improving breathing.
23. Balances Electrolytes
Magnesium works with potassium, sodium, and calcium to maintain proper electrolyte balance.
24. Boosts Metabolism
Magnesium plays a role in metabolizing carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
25. Supports Detoxification
Magnesium helps the liver detoxify harmful substances.
26. Improves Hair Health
Magnesium oil stimulates hair follicles, promoting hair growth and reducing hair loss.


27. Aids in Relaxation
Magnesium’s calming effects help combat fatigue, restlessness, and tension.
Magnesium Oil and DIY Magnesium Spray
Magnesium oil is a popular topical solution made from magnesium chloride and water. It’s applied directly to the skin for quick absorption, bypassing the digestive system.
DIY Magnesium Spray Recipe
Ingredients:
- 1/2 cup magnesium chloride flakes.
- 1/2 cup distilled water.
Instructions:
- Heat the water in a small pot until warm (but not boiling).
- Dissolve the magnesium chloride flakes in the warm water, stirring until fully dissolved.
- Pour the mixture into a spray bottle.
- Use the spray on your skin daily, focusing on areas prone to tension or soreness.
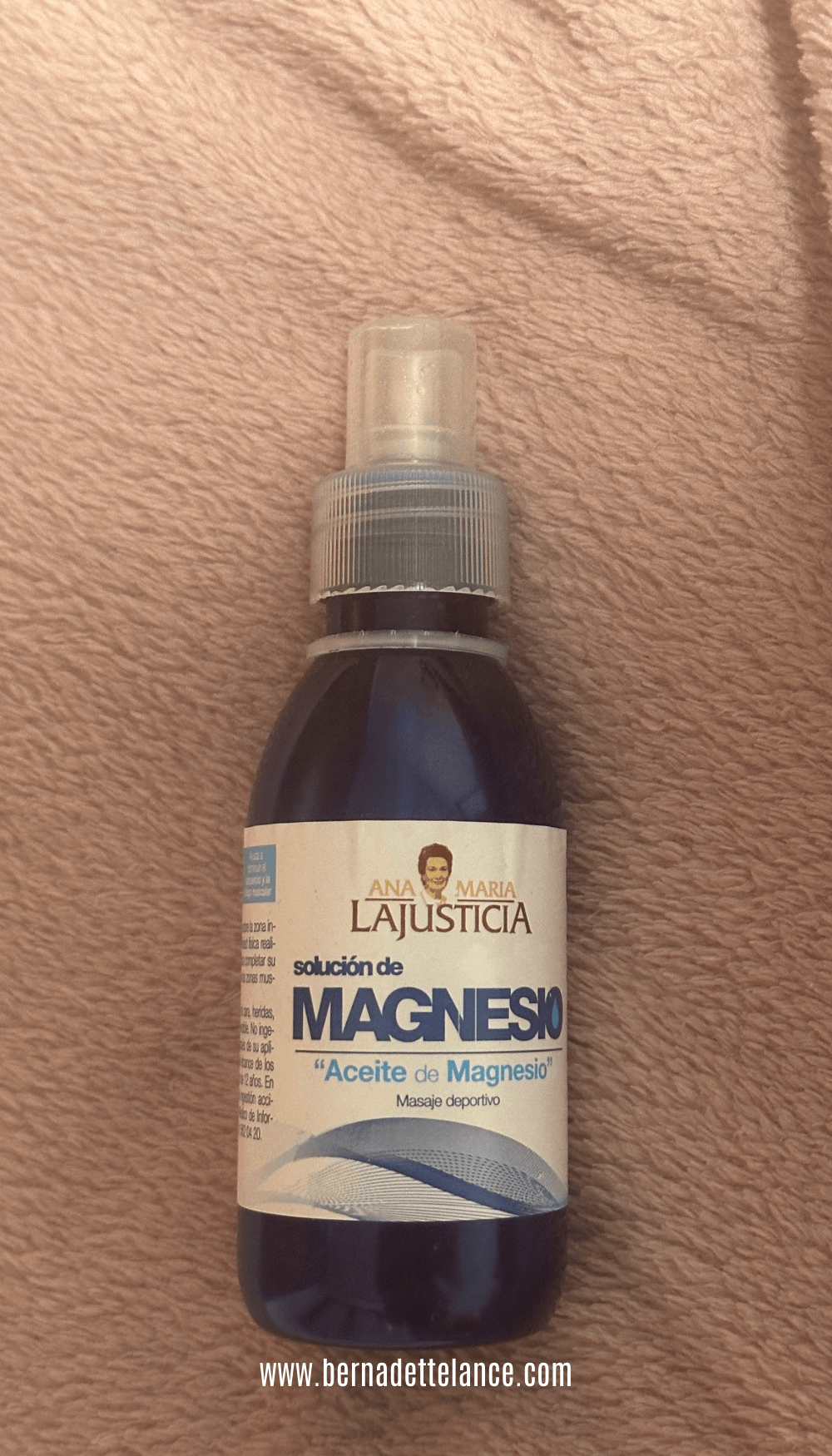

Additionally, you can purchase it already done, I love this one by Ana María La Justicia.
Magnesium Lotion: A Soothing Option
Magnesium lotion combines the benefits of magnesium oil with moisturizing ingredients like shea butter or coconut oil. It’s an excellent option for people with sensitive skin or those seeking hydration alongside magnesium supplementation.
Best Practices for Magnesium Supplementation
- Dosage: Adults typically need 300–400 mg of magnesium daily, but consult a doctor for personalized recommendations.
- Timing: Take magnesium glycinate at night for better sleep or magnesium citrate in the morning for digestive support.
- Consistency: Use magnesium sprays, oils, or lotions regularly for maximum benefits.


Magnesium’s Role in Stress Management
In today’s fast-paced world, stress has become a common part of daily life, and magnesium plays a crucial role in helping the body cope. When you’re stressed, your body rapidly depletes magnesium reserves, which can worsen symptoms of anxiety, fatigue, and muscle tension. Magnesium helps regulate the release of stress hormones like cortisol and supports the production of GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid), a neurotransmitter that promotes relaxation and calmness. Incorporating magnesium glycinate into your routine can be particularly beneficial for stress relief, as it is gentle on the stomach and highly absorbable, making it an ideal choice for calming the mind and body.


Magnesium for Long-Term Health
Beyond its immediate benefits, magnesium is essential for long-term health and disease prevention. Research has shown that adequate magnesium intake may reduce the risk of chronic conditions such as type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and osteoporosis. By improving insulin sensitivity, magnesium helps regulate blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of diabetes. Similarly, its role in maintaining healthy blood pressure and reducing inflammation protects the heart and blood vessels from damage. Regularly consuming magnesium-rich foods and using supplements like magnesium oil or magnesium lotion can contribute to a healthier, more resilient body as you age. Prioritizing magnesium as part of your wellness plan is a simple yet powerful step toward achieving optimal health and vitality.
FAQ About Magnesium
1. What is magnesium, and why is it important?
Magnesium is an essential mineral involved in over 300 enzymatic reactions in the body. It helps regulate muscle and nerve function, supports a healthy immune system, maintains heart health, and strengthens bones. Magnesium is also crucial for energy production and mental well-being.
2. What are the symptoms of magnesium deficiency?
Symptoms of magnesium deficiency include muscle cramps, fatigue, weakness, irregular heartbeat, insomnia, anxiety, headaches, poor digestion, and high blood pressure. Long-term deficiency can lead to more severe health issues like osteoporosis or cardiovascular disease.
3. What are the best sources of magnesium?
Magnesium-rich foods include leafy greens (spinach, kale), nuts (almonds, cashews), seeds (pumpkin seeds, flaxseeds), legumes (black beans, lentils), whole grains, dark chocolate, avocados, and seafood like salmon.
4. What are the benefits of magnesium oil or magnesium spray?
Magnesium oil, a solution of magnesium chloride and water, is applied topically to the skin. It helps relieve muscle cramps, promote relaxation, and improve magnesium levels without upsetting the stomach. It’s ideal for people who prefer not to take oral supplements.
5. Can I take magnesium daily?
Yes, magnesium can be taken daily, either through diet or supplements. The recommended daily intake is around 310-420 mg for adults, depending on age and gender. However, consult a healthcare provider to determine the correct dosage for your needs.
6. What are the benefits of magnesium glycinate?
Magnesium glycinate is one of the most bioavailable forms of magnesium, meaning it’s easily absorbed and gentle on the stomach. It’s commonly used to improve sleep quality, reduce anxiety, and support relaxation.
7. How can I make a DIY magnesium spray?
To make a magnesium spray, dissolve 1/2 cup of magnesium chloride flakes in 1/2 cup of warm distilled water. Stir until fully dissolved and pour the solution into a spray bottle. Apply directly to the skin for quick absorption.
8. What is the difference between magnesium citrate and magnesium glycinate?
Magnesium citrate is often used as a natural laxative to relieve constipation, while magnesium glycinate is more effective for relaxation, sleep improvement, and reducing anxiety. The choice depends on your specific health goals.
9. Can magnesium help with sleep?
Yes, magnesium plays a key role in calming the nervous system and regulating melatonin, the hormone responsible for sleep. Magnesium glycinate is particularly effective for improving sleep quality.
10. Is it safe to use magnesium during pregnancy?
Magnesium is generally safe and beneficial during pregnancy, as it supports fetal development and reduces the risk of complications like preeclampsia. However, pregnant women should consult their healthcare provider before taking magnesium supplements.
Contraindications and Precautions for Magnesium Use
While magnesium is generally safe, there are certain situations where caution is needed:
1. Kidney Disease
People with kidney problems or chronic kidney disease should avoid high doses of magnesium. Impaired kidneys may struggle to filter out excess magnesium, leading to toxicity.
2. Low Blood Pressure (Hypotension)
Magnesium can relax blood vessels and lower blood pressure. While this is beneficial for people with hypertension, it may cause complications in individuals with already low blood pressure.
3. Interactions with Medications
Magnesium may interact with certain medications, including:
- Antibiotics: Magnesium can reduce the effectiveness of some antibiotics like tetracyclines and fluoroquinolones.
- Diuretics: These medications may increase magnesium loss through urine.
- Bisphosphonates: Used for osteoporosis, these drugs may have reduced absorption if taken with magnesium.
- Heart Medications: High doses of magnesium can interfere with medications that regulate heart rhythm. Always consult your healthcare provider before combining magnesium with medications.
4. Overuse or High Dosages
Taking too much magnesium, particularly in supplement form, can lead to adverse effects, such as:
- Diarrhea (common with magnesium citrate or magnesium oxide).
- Nausea.
- Abdominal cramping.
- In severe cases, magnesium toxicity, which may cause irregular heartbeat, low blood pressure, difficulty breathing, or cardiac arrest.
5. Allergies
While rare, some individuals may experience an allergic reaction to magnesium supplements or topical magnesium products like sprays or lotions. Signs include skin irritation, rash, or itching.
6. Heart Block or Myasthenia Gravis
Individuals with certain heart conditions, such as heart block, or neuromuscular disorders like myasthenia gravis should consult a doctor before using magnesium, as it can further relax muscles and impair function.
7. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Although magnesium is generally safe for pregnant and breastfeeding women, dosage recommendations may differ. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting supplements during these periods.
8. Children
Magnesium supplements should be used cautiously in children, and only under the guidance of a pediatrician, as dosage requirements vary based on age and weight.
Final Word on Safety
Magnesium is an essential nutrient with numerous health benefits, but like any supplement, it should be used mindfully. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting a magnesium regimen, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications. By following guidelines and monitoring your body’s response, you can safely enjoy the wide-ranging benefits of magnesium.
Conclusion
Magnesium is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in maintaining physical and mental health. From supporting energy production to promoting relaxation and reducing inflammation, its benefits are vast and well-documented. Whether you’re consuming magnesium-rich foods, using magnesium sprays, or applying magnesium lotion, this powerhouse mineral can significantly improve your quality of life.
By addressing magnesium deficiency symptoms early and incorporating magnesium into your routine, you can unlock its full potential and enjoy a healthier, more balanced lifestyle. So why wait? Start reaping the incredible benefits of magnesium today!